 |
 |
- Search
| Anesth Pain Med > Volume 17(3); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Notes
FUNDING
This work was supported by the Korea Medical Device Development Fund grant funded by the Korean government (the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety) (Project Number: KMDF_PR_20200901_0031, 202011B25-01).
Fig. 1.
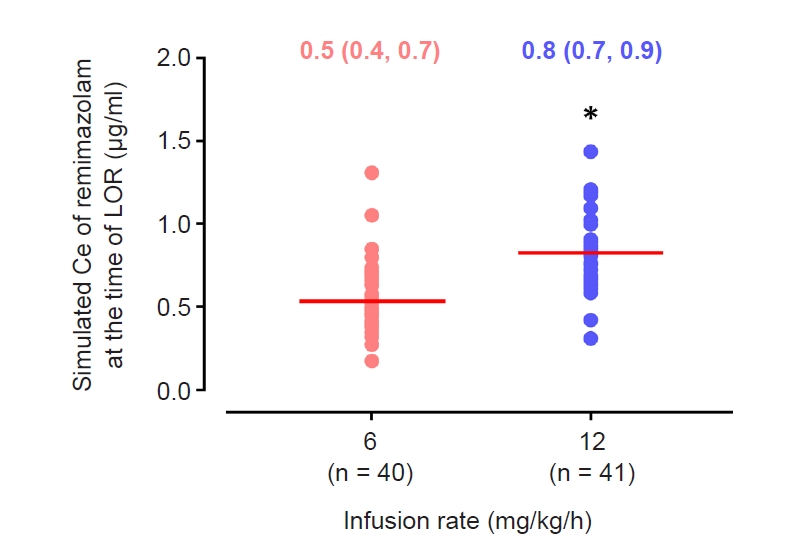
Fig. 2.
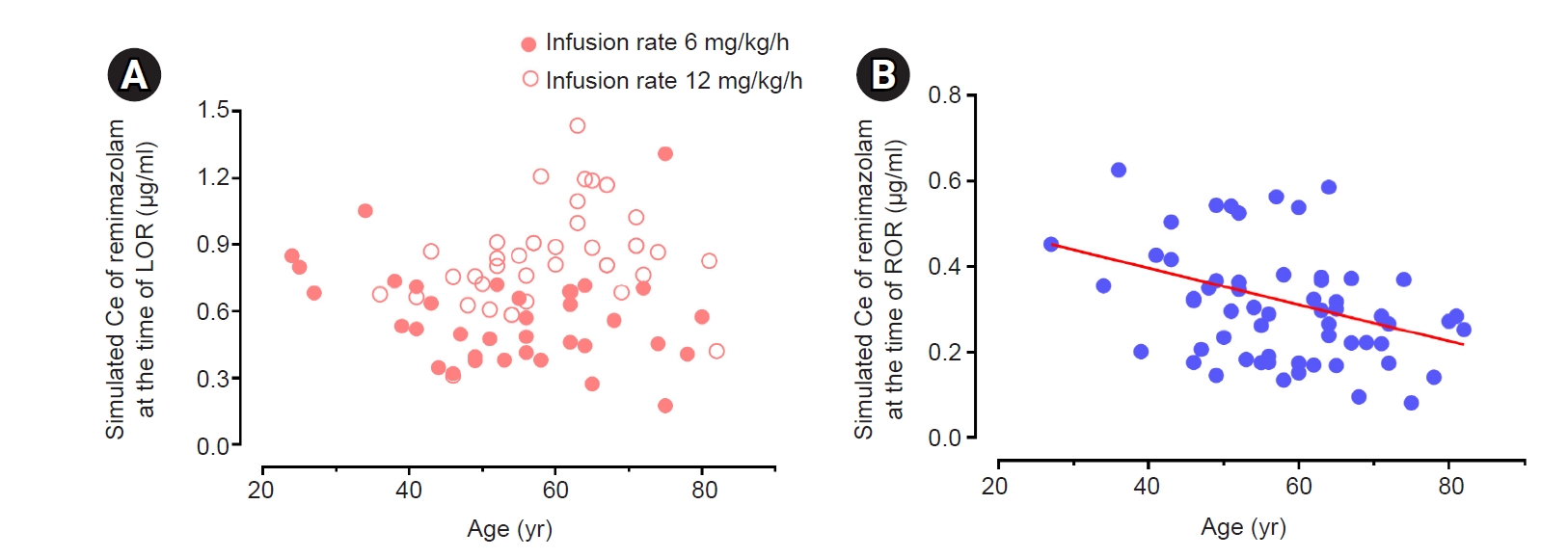
Fig. 3.
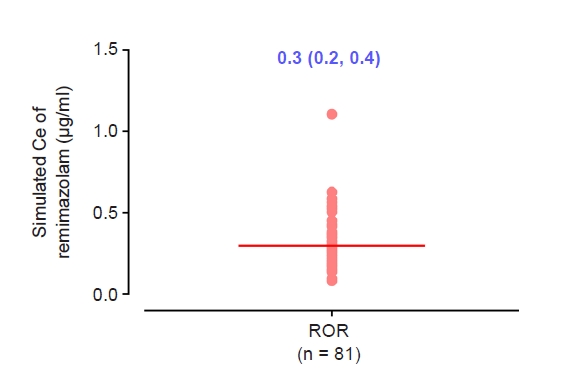
Fig. 4.
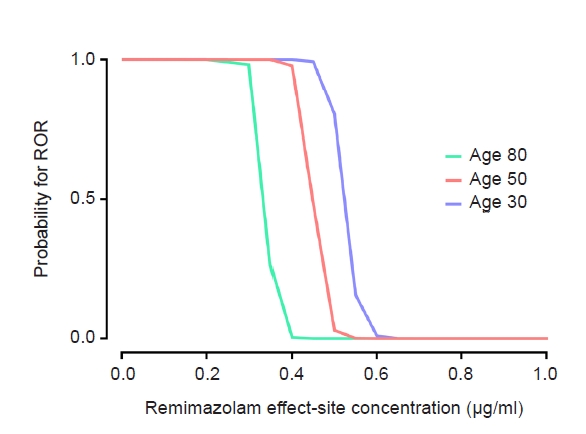
Table 1.
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| V1 (L) | 0.0627 × body weight |
| V2 (L) | 14.5 |
| V3 (L) | 15.5 |
| CL (L/min) | 1.14 |
| Q2 (L/min) | 1.04 |
| Q3 (L/min) | 0.19 |
| ke0 (1/min) | 0.27 |
V1: central volume of distribution, V2: rapid peripheral volume of distribution, V3: slow peripheral volume of distribution, CL: clearance, Q2: inter-compartmental clearance of rapid peripheral compartment, Q3: inter-compartmental clearance of slow peripheral compartment. Pharmacokinetic parameters and ke0 from the Schüttler model [13]. The ke0 was estimated against Modified Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale.
Table 2.
Data are expressed as mean ± SD, median (1Q, 3Q), or count as appropriate. ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists. Mean infusion rate during anesthesia maintenance was calculated as follows:
Table 3.
Non-parametric bootstrap analysis was repeated 2,000 times. RSE indicates relative standard error = SE/mean × 100 (%); CV: coefficient of variation; RSE: relative standard error = SE/estimate × 100 (%), CV: coefficient of variation, OFV: objective function value, Ce50,ROR: effect-stie concentration of remimazolam, associated with 50% probability for recovery of responsiveness; γ: steepness of the concetration-response curve, ROR: loss of responsiveness, CI: confidence interval.
REFERENCES
-
METRICS

-
- 9 Crossref
- 3,505 View
- 90 Download
- Related articles in Anesth Pain Med
- ARTICLE & TOPICS
-
- Topics
-
- Neuroscience in anesthesiology and critical care
- Anesthetic Pharmacology
- Obstetric Anesthesia
- Pediatric Anesthesia
- Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia
- Transplantation Anesthesia
- Spinal Pain
- Regional Anesthesia
- Neuromuscular Physiology and Pharmacology
- Airway Management
- Geriatric anesthesia and Pain
- Others